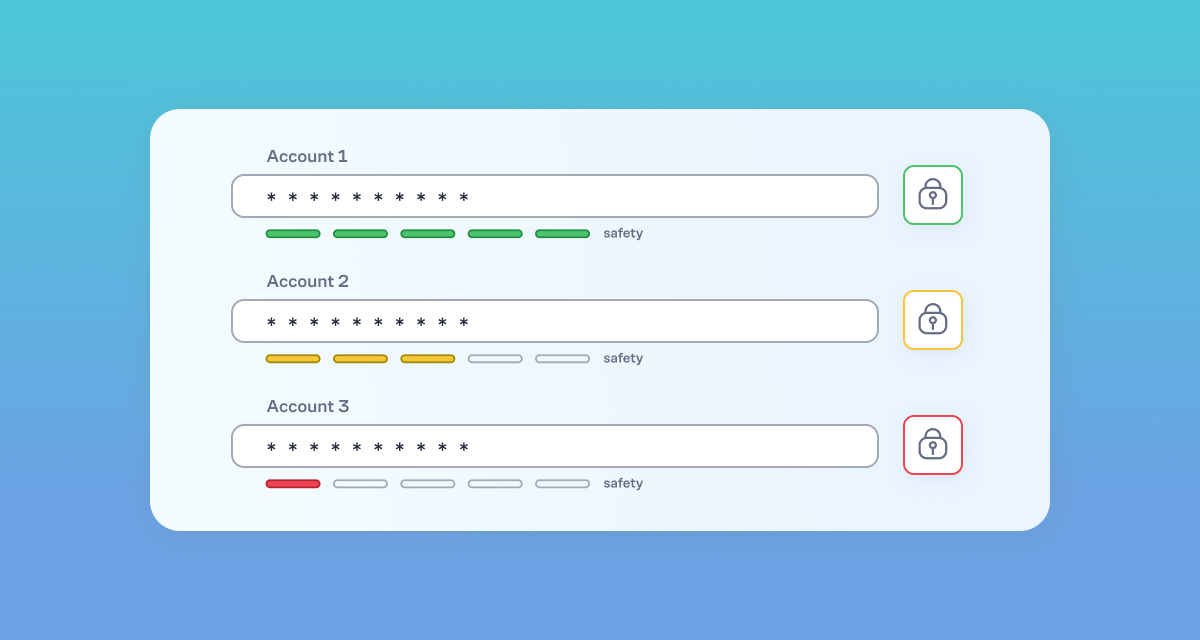
In the age of digital information, the use of passwords has become a routine part of our daily lives. From personal emails and social media to online banking and shopping, passwords act as the gatekeepers to our most sensitive data. Using the same password across various platforms may be tempting, but it conceals the danger of password reuse, putting our digital security at significant risk.
Quick facts on the dangers of password reuse
- 30% of internet users have experienced a data breach due to a weak password.
- Two-thirds of Americans use the same password across multiple accounts.
- The most commonly used password is “123456.”
- 59% of US adults use birthdays or names in their passwords.
- 13% of Americans use the same password for every account.
Why Using The Same Password For Multiple Accounts is a Dangerous Practice

Using the same password across multiple accounts poses a significant security risk, creating a potential domino effect of vulnerabilities. When one account is compromised, it opens the door to a cascade of breaches, jeopardizing your entire digital identity. Let's explore the dangers of password reuse across accounts.
Single point of failure
Using the same password for multiple accounts creates a single point of failure in your security system. If a cybercriminal manages to uncover the password to one of your accounts, they can access all your other accounts that use the same password. This opens the door to an extensive breach of your personal and financial data. The risks are even higher if the compromised account is linked to your email, which often serves as a recovery point for many other accounts.
Data breaches and password leaks
Every now and then, we hear about data breaches from large corporations, resulting in millions of leaked usernames and passwords. If your password is among the leaked ones and you use it for multiple accounts, cybercriminals can use this information to access your other accounts. They use a technique known as "credential stuffing", where leaked username/password pairs are tested against multiple online platforms.
Predictable password patterns
Often, when individuals use the same password for multiple accounts, they tend to create minor variations for different sites. Cybercriminals are aware of this habit and use sophisticated algorithms to predict these variations. This makes all your accounts susceptible to hacking even if you believe you have made them distinct enough.

Reduced effectiveness of two-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a robust security measure that adds an extra layer of protection to your accounts. However, if you are using the same password across multiple platforms, the effectiveness of 2FA is reduced. A hacker who gains access to one account may also be able to bypass 2FA on other platforms, especially if your secondary authentication information is accessible through the already breached account.
Compromised privacy and identity theft
Reusing passwords makes it easier for cybercriminals to invade your privacy and potentially steal your identity. They can access your personal information, financial details, and more, leading to severe consequences such as unauthorized transactions or even fraudulent activities conducted in your name.
How To Protect Yourself From Password Reuse
The dangers of password reuse far outweigh the convenience it offers. Instead, prioritize your digital security by adopting good password and login security practices.
#1 - Use a unique and strong password for every account
Adopt a practice of creating distinctive and robust passwords for each of your accounts. This proactive measure ensures that even if one password is compromised, the security of your other accounts remains intact, mitigating the risk of widespread breaches.
Hundreds of Agencies Across The World Use LLAR





#2 - Enable two-factor authentication whenever possible
Elevate your account security by implementing two-factor authentication (2FA). This additional layer of protection requires users to verify their identity through a secondary method, such as a mobile app or SMS. Studies show that accounts with 2FA are significantly less susceptible to unauthorized access, providing an effective defense against potential security threats.
#3 - Reduce the amount of authorized users on your online accounts
Regularly assess and scrutinize the user activity across your online accounts, particularly those housing sensitive information. It might not be the admin that has poor password policies, but the additional users on the account. Ensure that login security tools are installed on your websites designed to prevent unauthorized logins and limit login attempts, such as the utilization of plugins like Limit Login Attempts Reloaded.
#4 - Regularly update your passwords
Stay ahead of potential security risks by routinely updating your passwords. Schedule this on your calendar every 3-6 months so it's not forgotten. Cybersecurity incidents often exploit outdated credentials, making regular password changes a crucial defense mechanism.
#5 - Use a reputable password manager to remember your passwords
Simplify and strengthen your password management with a reputable password manager. These tools not only help you generate and store complex passwords securely but also streamline the process of accessing your accounts. By entrusting your password management to a reliable solution, you ensure that your credentials are both strong and conveniently accessible, contributing to a robust security strategy.
Conclusion
Remember, in the digital world, your password is often the first line of defense against cyber threats. It's essential to keep it strong and unique to safeguard your digital assets effectively. By following the above steps, you'll be more prepared about the dangers of password reuse. Be smart about your password habits - your digital security depends on it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Using the same password across multiple accounts poses a significant risk because if one account is compromised, it puts all linked accounts in jeopardy. Cybercriminals often exploit this practice to gain unauthorized access to multiple platforms, potentially leading to widespread data breaches and identity theft.
Password reuse weakens the effectiveness of individual account security measures. When a password is compromised on one platform, the likelihood of unauthorized access increases across other accounts with the same password. This undermines the security protocols put in place by individual platforms, leaving users more vulnerable to cyber threats.
To protect against the dangers of password reuse, individuals should adopt security practices such as using unique passwords with at least 12 characters for each account, enabling two-factor authentication, and regularly updating passwords. Additionally, employing a reputable password manager can enhance overall security by generating and storing complex passwords securely.